The Importance of Vital Signs
Vital signs are essential indicators of a person’s overall health and well-being. They provide valuable information about various physiological functions and help healthcare professionals assess a person’s current condition. Understanding and monitoring vital signs play a crucial role in healthcare settings, emergency situations, and even in daily life.

What Are Vital Signs?
Vital signs refer to a set of measurements that reflect the basic functions of the body. These measurements include body temperature, heart rate, blood pressure, and respiratory rate. Each vital sign provides valuable insights into different aspects of a person’s health.
Vital Sign and Measurement
Body Temperature: Measured in degrees Fahrenheit (°F) or Celsius (°C)
Heart Rate: Measured in beats per minute (bpm)
Blood Pressure: Measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg)
Respiratory Rate: Measured in breaths per minute (bpm)
Why Are Vital Signs Important?
Vital signs are important for several reasons. First and foremost, they serve as indicators of a person’s overall health status. Any significant deviation from normal ranges may suggest an underlying health condition or a change in the body’s functioning.
Monitoring vital signs is particularly crucial in medical settings. They provide healthcare professionals with critical information to assess a patient’s condition and make informed decisions regarding treatment and care. For example, changes in heart rate or blood pressure may indicate a need for immediate medical intervention.
In emergency situations, vital signs become even more critical. They help emergency responders quickly evaluate a person’s condition and prioritize medical care accordingly. Immediate attention can be given to individuals with abnormal vital signs, ensuring timely and potentially life-saving interventions.
Beyond medical environments, monitoring vital signs in daily life can also be beneficial. It allows individuals to track changes in their health over time, identify patterns, and take proactive measures to maintain or improve their well-being. For instance, tracking resting heart rate can help assess fitness levels and the effectiveness of exercise routines.
Understanding vital signs and their significance empowers individuals to be more proactive about their health and seek appropriate medical attention when necessary. By regularly monitoring and interpreting vital signs, individuals can play an active role in maintaining their well-being.
In the following sections, we will explore each vital sign in more detail, including their normal ranges, how to interpret them, and their relevance in different situations.
Understanding Each Vital Sign
Vital signs provide valuable information about the body’s overall health and function. In this section, we will explore the four primary vital signs: body temperature, heart rate, blood pressure, and respiratory rate.
Body Temperature
Body temperature is a measure of the body’s internal heat. It is influenced by various factors, including metabolism, environmental conditions, and illness. The normal range for body temperature can vary slightly depending on the method of measurement. The average normal range is as follows:
Age Group and Normal Body Temperature Range
Adults: 97.8°F – 99°F (36.5°C – 37.2°C)
Children: 97.9°F – 100.4°F (36.6°C – 38°C)
Heart Rate
Heart rate, also known as pulse rate, refers to the number of times the heart beats per minute. It is an essential indicator of cardiovascular health. The normal range for heart rate can vary depending on age and physical condition. Here are the approximate normal ranges for different age groups:
Age Group and Normal Heart Rate Range
Newborns: 70-190 beats per minute (bpm)
Infants (0-12 months): 80-160 bpm
Children (1-10 years): 70-120 bpm
Adults (over 10 years): 60-100 bpm
Blood Pressure
Blood pressure is a measure of the force exerted by blood against the walls of the arteries. It consists of two values: systolic pressure (the pressure when the heart contracts) and diastolic pressure (the pressure when the heart is at rest). The normal range for blood pressure is typically around 120/80 mmHg (millimeters of mercury), but it can vary depending on factors such as age and overall health.
Respiratory Rate
Respiratory rate refers to the number of breaths taken per minute. It provides insights into the efficiency of the respiratory system. The normal range for respiratory rate can vary depending on age and overall health. Here are the approximate normal ranges for different age groups:
Age Group and Normal Respiratory Rate Range
Newborns: 30-60 breaths per minute
Infants (0-12 months): 20-30 breaths per minute
Children (1-10 years): 15-30 breaths per minute
Adults (over 10 years): 12-20 breaths per minute
Understanding each vital sign and their normal ranges is crucial for identifying any deviations from the norm. However, it’s important to note that these ranges are general guidelines, and individual variations may exist. Regular monitoring of vital signs can help detect any potential health issues and allow for timely medical interventions if necessary.
Interpreting Vital Signs
When it comes to assessing a person’s health, understanding and interpreting vital signs is of utmost importance. Vital signs provide valuable information about the functioning of the body’s major systems. In this section, we will explore the normal ranges for vital signs and the meaning behind abnormal readings.
Normal Ranges for Vital Signs
Vital signs consist of several measurements, including body temperature, heart rate, blood pressure, and respiratory rate. Understanding the normal ranges for these vital signs is essential for determining whether an individual’s health is within expected parameters.
Vital Sign and Normal Range
Body Temperature: 97.8°F to 99°F (36.5°C to 37.2°C)
Heart Rate (Pulse): 60 to 100 beats per minute (bpm)
Blood Pressure: Less than 120/80 mmHg
Respiratory Rate: 12 to 20 breaths per minute
It’s important to note that the normal ranges may vary slightly depending on factors such as age, underlying health conditions, and individual differences. Consultation with a healthcare professional is recommended for a more accurate assessment.
Abnormal Vital Signs and Their Meaning
Abnormal vital signs can indicate underlying health issues or potential medical emergencies. Understanding the meaning behind abnormal readings is crucial for identifying when further medical attention is necessary.
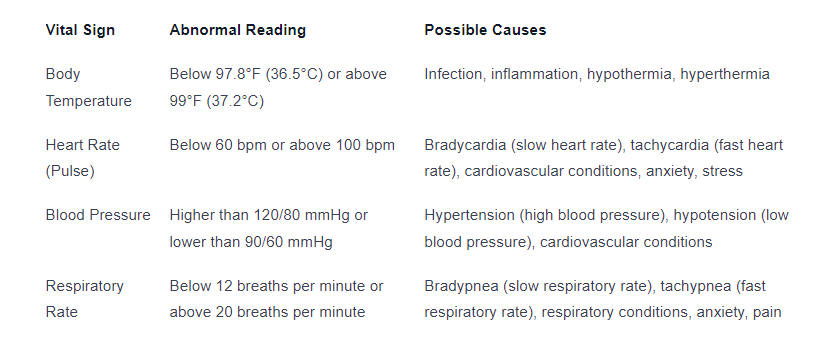
It’s important to remember that a single abnormal reading does not necessarily indicate a severe health problem. However, persistent or extreme abnormal vital signs should not be ignored and may require further evaluation by a healthcare professional.
Interpreting vital signs provides valuable insights into an individual’s overall health status. Regular monitoring and understanding of these vital signs can help detect potential health issues and prompt timely medical intervention when needed. If you notice any significant deviations from the normal ranges or have concerns about your vital signs, it’s advisable to seek medical attention for a thorough evaluation.
Vital Signs in Different Situations
Vital signs play a crucial role in monitoring and assessing a person’s overall health and well-being. They provide valuable information about the body’s physiological functions. Vital signs are monitored in various settings, including medical settings, emergency situations, and even in daily life.
Vital Signs in Medical Settings
In medical settings such as hospitals, clinics, and doctor’s offices, monitoring vital signs is an essential part of patient care. Healthcare professionals regularly measure and track vital signs to assess a patient’s current health status, detect any abnormalities or changes, and monitor the effectiveness of treatments or medications.
Here are the normal ranges for vital signs in a medical setting:
Vital Sign and Normal Range
Body Temperature: 97.8°F – 99°F (36.5°C – 37.2°C)
Heart Rate: 60 – 100 beats per minute
Blood Pressure: Less than 120/80 mmHg
Respiratory Rate: 12 – 20 breaths per minute
These ranges can vary slightly depending on factors such as age, gender, and overall health. It’s important for healthcare professionals to interpret vital signs within the context of the individual patient’s baseline and medical history.
Vital Signs in Emergency Situations
During emergency situations, vital signs are crucial for assessing the severity of a person’s condition and determining the appropriate course of action. Emergency medical personnel rely on vital signs to make quick decisions and provide immediate care.
In emergency situations, vital signs are monitored more frequently, and any significant changes can indicate a worsening condition or the need for immediate intervention. It’s important to note that abnormal vital signs in an emergency setting may require immediate medical attention.
Vital Signs in Daily Life
While vital signs are commonly associated with medical and emergency settings, they can also be monitored in daily life. Some individuals may monitor their vital signs at home as a proactive measure for maintaining their health or managing certain medical conditions.
For example, individuals with chronic conditions such as hypertension or diabetes may regularly measure their blood pressure or blood glucose levels. This self-monitoring can provide valuable information for managing their conditions and alert them to any changes that may require medical attention.
It’s essential to remember that while monitoring vital signs in daily life can provide insights, it should not replace regular medical check-ups or professional medical advice. Consulting with a healthcare provider is important for comprehensive and accurate assessment of one’s health.
Understanding vital signs in different situations allows individuals and healthcare professionals alike to stay informed about their health status and make informed decisions regarding their well-being. Regular monitoring of vital signs can provide valuable information and early detection of any potential health concerns.
How to Monitor Vital Signs
Monitoring vital signs is an essential aspect of healthcare and can provide crucial information about a person’s overall health. Whether it’s for routine check-ups or during emergency situations, accurate measurement of vital signs is vital for proper medical assessment. In this section, we will explore the tools and equipment used for monitoring vital signs, provide tips for accurate measurement, and discuss when to seek medical attention based on abnormal vital signs.
Tools and Equipment for Monitoring Vital Signs
Healthcare professionals use various tools and equipment to monitor vital signs accurately. Here are some commonly used devices:
- Thermometer: A thermometer is used to measure body temperature. There are different types of thermometers, including oral, ear, forehead, and digital thermometers.
- Stethoscope: A stethoscope is an instrument used to listen to the sounds produced by the heart, lungs, and other internal organs. It helps healthcare providers assess heart rate, respiratory rate, and certain abnormalities.
- Blood pressure monitor: A blood pressure monitor measures the force exerted by blood against the walls of the arteries. There are manual blood pressure monitors (sphygmomanometers) and automatic electronic blood pressure monitors.
- Pulse oximeter: A pulse oximeter is a non-invasive device that measures the oxygen saturation level in the blood. It also provides information about heart rate.
Tips for Accurate Measurement
To ensure accurate measurement of vital signs, consider the following tips:
- Proper technique: Follow the instructions provided with each device to ensure correct usage. For example, take care to position the blood pressure cuff properly, place the stethoscope correctly, and maintain a consistent environment for temperature measurements.
- Relaxation: Encourage the person being monitored to relax and remain still during the measurement. Physical activity, stress, or anxiety can affect vital sign readings.
- Consistency: Maintain consistency in the measurement process by using the same equipment, technique, and time of day whenever possible. This helps in tracking changes accurately over time.
- Multiple measurements: Take multiple measurements to ensure reliability and identify any variations. For instance, measure blood pressure on both arms or take multiple temperature readings to confirm accuracy.
When to Seek Medical Attention Based on Vital Signs
Abnormal vital signs can indicate underlying health issues. While specific thresholds for seeking medical attention may vary depending on individual factors and medical history, it’s generally recommended to consult a healthcare professional if you experience any of the following:
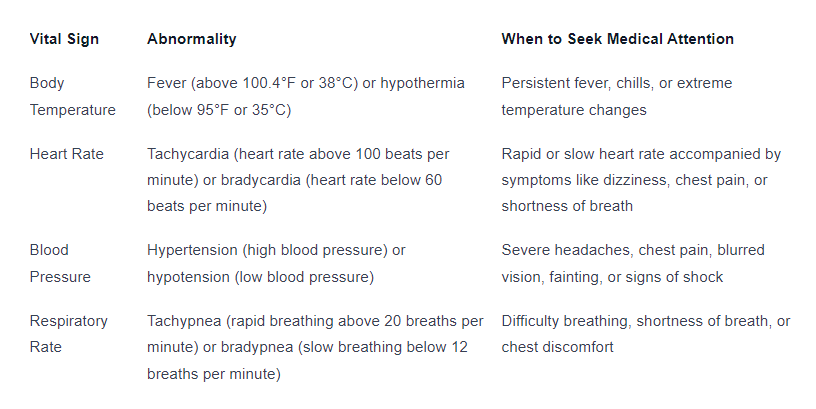
It’s important to remember that vital signs can vary based on factors such as age, gender, physical activity, and overall health. Regularly monitoring your vital signs and being aware of any significant changes can help you take appropriate action and seek medical attention if necessary.
Sources
Vital signs: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia



